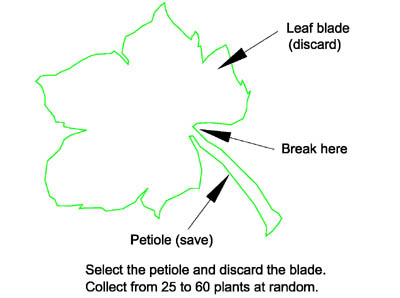
Plant Tissue Sampling Procedure
Plant tissue analysis is primarily used to detect nutrient deficiencies and to evaluate responses to fertilizer additions and other cultural practices. Both soil testing and plant analysis are useful diagnostic tools and one should not be used in lieu of the other. Similar to soil testing, an important aspect of plant analysis is sample collection and handling. Plant composition varies with age, plant part, plant condition, variety, and environmental factors. Therefore, it is essential that proper sampling protocols be followed.
These guidelines should be consulted prior to sampling any crop to ensure proper interpretation and meaningful results. Separate sampling and analyses should be conducted in those areas that appear to differ greatly from the rest of the field. This same approach should also be used when conducting diagnostic or troubleshooting procedures.
It is also important to identify what not to include in a tissue sample. Plants that are under stress, or mechanically or insect damaged, or disease infested should not be sampled. Finally, it is desirable to withhold sampling during, or immediately following (i.e., a few days), an irrigation event.
Use a clean container such as a paper bag or a plastic pail when collecting a tissue sample. Never use a metal container due to the risk of sample contamination. Avoid placing tissue samples in a plastic bag unless the bag is vented or the sample is refrigerated.
Once a tissue sample has been collected, it should be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible. Do not store plant tissue samples in air-tight bags or at room temperature. Keep plant tissue samples cool (refrigerator temperature) but do not freeze.
Accurate plant sampling requires experience and knowledge, therefore, the use of trained and experienced samplers is strongly recommended.
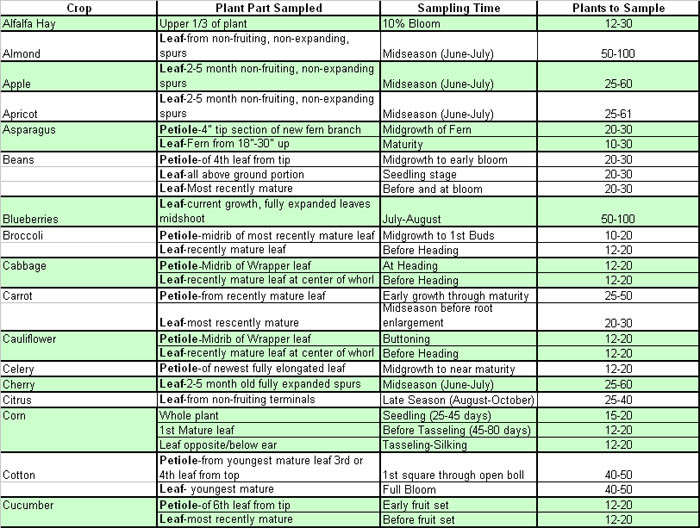
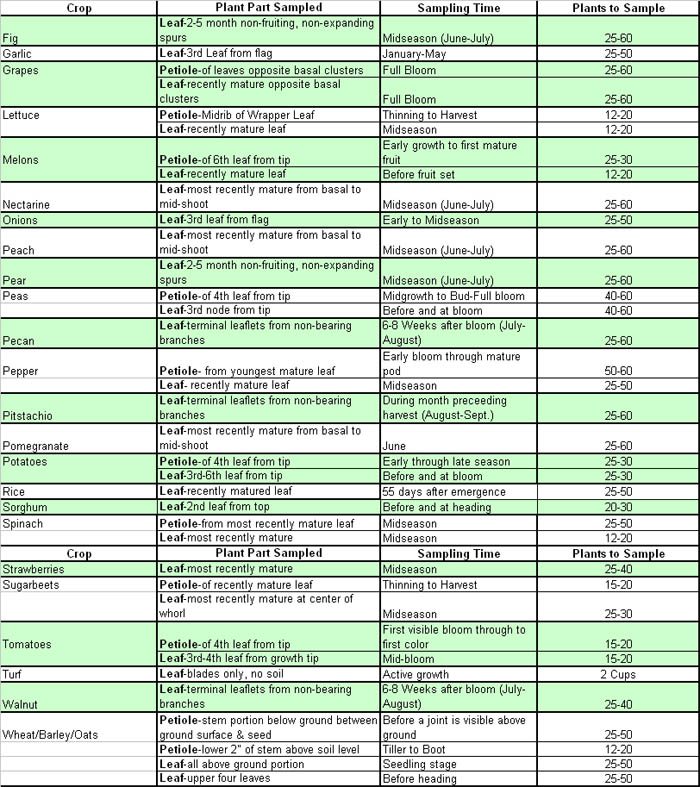
Desired sample locations for common crops and a table presenting an outline the appropriate sample times, plant parts, and sample sizes pertaining to plant tissue collection for various crops follow.
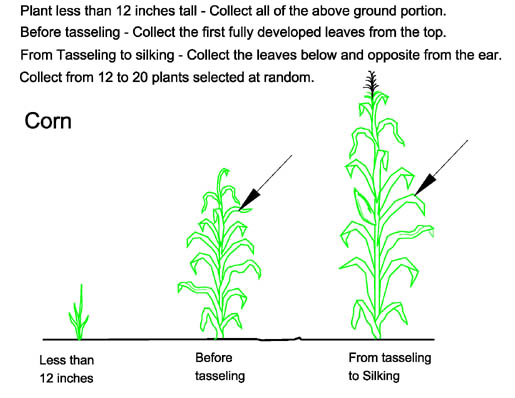
Corn Model
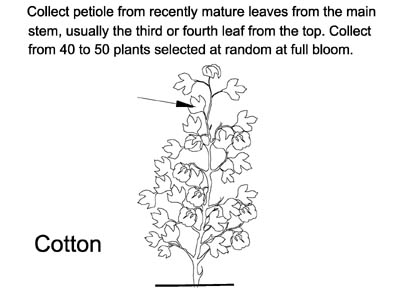
Cotton Model
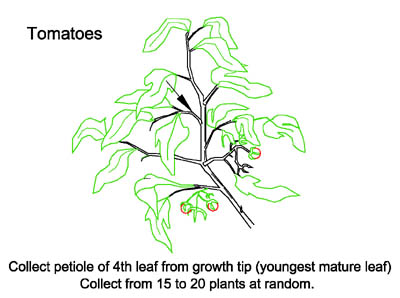
Tomato Model
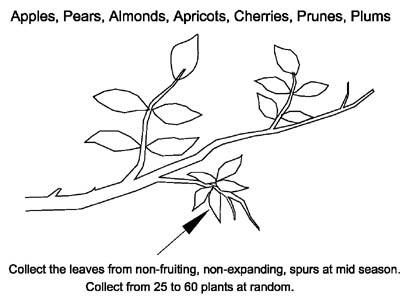
Tree S-1 Model
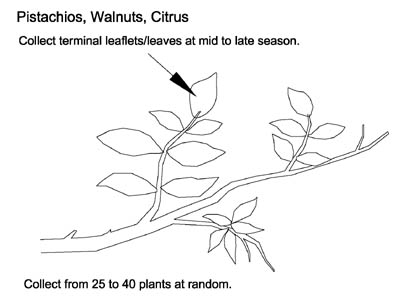
Tree S-2 Model

Tree S-3 Model
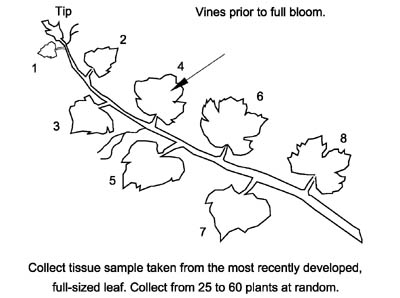
Vine Model – Prior to Full Bloom
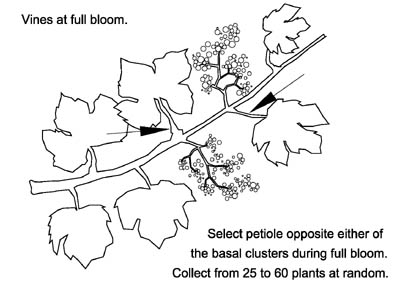
Vine Model – Full Bloom
Vine Model Petiole